Authors: Margherita Ceserani, Will Kingston-Cox, Ilaria Lorusso, Shahin Modarres
Russia’s war in Ukraine has reached its 398th day and the pro-Russian mercenary Wagner Group is still engaging in the battlefield of Bakhmut, in the Donetsk province, after eight months of combat. They have been assaulting the city since August 2022 and, even though they succeeded on the East frontline, there is still room for a defeat by hands of the Ukrainian resistance backed by three Mi-8 helicopter gunships.
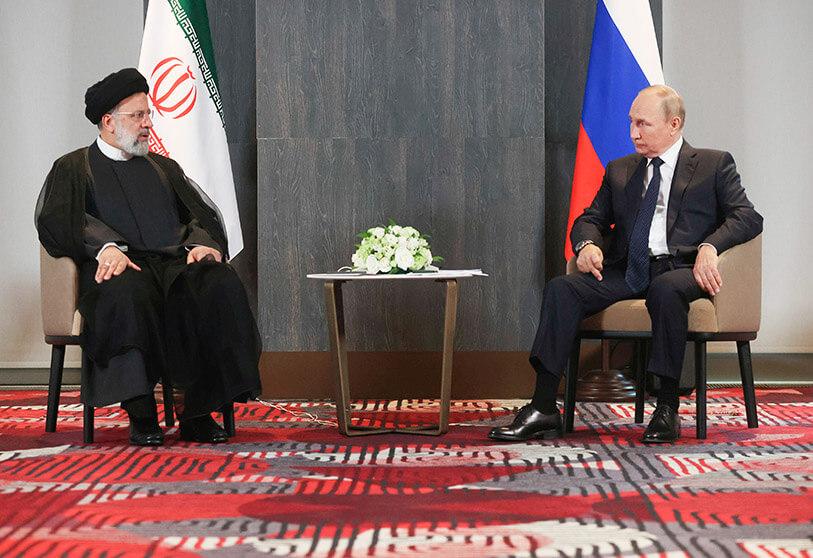
That the war was also being conducted from the air is not news as several sources confirmed the deployment of Iranian drones serving the Russian army, although information was repeatedly denied by Tehran. Moreover, Iran has just confirmed a deal through which it will be in receipt of three SU-35 fighter planes from Russia. This signals two trends: firstly, the Iranian intention to reconstitute its military arsenal and to strengthen its aircraft forces; ultimately, its willingness to develop a weapon market and become a relevant seller, given that the embargo on ballistic missile commerce is expiring in October 2023.
The ties with Moscow have been growing increasingly close. Indeed since the rapprochement in 1989, the interests of the two Eastern powers have often converged, for example, on critiques of Western sanctions and the JCPOA. Today, the presence of Iranian personnel in Ukraine has the double aim of bringing support, training and know-how to Russian soldiers employing Iranian kamikaze drones, observing their functioning, and finding vulnerabilities to be improved. How do the military doctrines of these two countries meet? What should we expect from their bilateral relationship?
Russia’s military doctrine can be defined by its active pursuit of modernization and expansion in Russian military capabilities, such as investing in new weapons systems and conducting full-scale military exercises. The current doctrine–adopted in 2014–enshrines the importance of securing Russia’s borders and Moscow’s interests overseas, as well as the maintenance of the Kremlin’s strategic nuclear deterrence, vis-à-vis the identification of NATO and the United States' expansion of its missile capacity as a significant threat to Russia’s national security. It also contains the concept of ‘strategic deterrence’, which seeks to deter adversaries from attacking Russia under the notion that Moscow is willing to employ ‘preemptive strikes’ wherever it deems necessary
Similarly, the military doctrine of Iran is centred around the principles of defence and deterrence. Iranian military authorities emphasize the importance of perpetuating a strong, unwavering defensive position to deter potential threats and defend Iran’s territorial sovereignty against external belligerence. The doctrine’s latest update, in 2018, identifies the importance of enhancing and refining Iran’s military capabilities–both conventional and asymmetric–to advance the end goal of protecting Iranian territorial integrity.
The convergence of Russian and Iranian military doctrines through security cooperation is not a new phenomenon. For example, both Tehran and Moscow supported Bashar al-Assad in Syria to assert their geopolitical interests and strategic partnership in the region. However, in the context of the Russo-Iranian strategic partnership vis-à-vis the Ukrainian invasion, we can identify a greater synthesis of the military doctrines of Tehran and Moscow and their respective political and economic objectives. The war in Ukraine provides another dimension to the Russo-Iranian strategic cooperation.

Both Russia and Iran find themselves increasingly isolated from the international community. Thus, strategic military cooperation provides unparalleled economic and political relief for the two ‘quasi-pariahs’. Russia, now a state proficient in the avoidance of sanctions, has been keenly training their Iranian counterparts the same techniques so as to continue fruitful trade between the two nations. Through the provision of loitering munitions–“kamikaze” drones–to Russia on the Ukrainian battlefields, Iran is hopeful it can alleviate the pressures of its current economic position–a position exponentially compounded by sanctions imposed by the West, as well as a metaphoric flex of muscles to its regional adversaries.
For Moscow, importing Iranian drones provides a cheap and effective method of carrying out its strategic goals in Ukraine. Costing roughly $20,000 per unit, Iranian “kamikaze” drones, such as the Shahed-136, strategically emboldens Putin’s war machine at little significant cost to Moscow. The capability of devastation loaded to these drones, however, should not be underexaggerated. Not only does ‘strategically cooperating’ with Iran alleviate the pressures of drone production on a beleaguered Russian economy, but it also perpetuates the likelihood of Russian attacks on Ukrainian civilian infrastructure.
The so-called strategic cooperation between the Islamic Republic and Russia is in reality, mostly a one-way pact in favour of the Kremlin. Russia has backed its allies, such as Syria and Belarus to suppress the protests ruthlessly. In this case regarding Iran, Russian intervention can be divided into three categories:
- Sending forces, which is not possible considering the serious lack of forces on the Ukrainian front. It is also crucial to mention that officials such as Sergei Surovikin who is one of the very few suitable forces to have such a role is now the new commander of the Russian forces in Ukraine.
- Intelligence and Security cooperation, which precedent shows cannot exceed a certain level as it is a double-edged blade. Such cooperation in precedent was provided for Ba’ath movement in the Arab world but never exceeded a certain limit
- Disinformation and #propaganda support, for which Russia holds the first place in the world but has already offered its best to the Islamic Republic.
Hence, it should not be a point that can discourage the Iranian people. Also, the international community is closely following the Tehran-Kremlin affairs. They will respond to such cooperation under many causes, making them take more serious positions regarding Iran's atrocious human rights violations.
The Islamic Republic’s interest in Russia is mostly based on three main elements. The first element is cooperation regarding the development of satellite technologies because the Islamic republic wants to save its three satellite positions and benefit from Russian satellites, not only for communication means but also for espionage. The second element to consider is Islamic republics’ dependency on the Russian campaign and models of disinformation, which they try to apply within the country. Finally, the third reason is their #intelligence cooperation and their need for structural support from Russia.
Beyond these three elements, we should consider something called “the mad king phase, " a state where it’s a totalitarian system, before its demise, tends to commit grave strategic mistake after strategic mistake.
The response by the international community can only manoeuvre a little on the particular matter of drones because of legal technicalities that make this matter quite hard to analyze. However, it is crucial to consider that the political will to oppose the affluence of the Islamic republic will become much stronger, more systematic, and more collective.
Ukraine’s best strategy to counter the drones made by the Islamic Republic can come from a country that has been studying them for quite a few years. Israel has developed both #IronDome and IronBeam at the Rafael Company by precisely studying and developing mathematical models of the technologies that were used in most of the missiles and drones that came from Gaza and Lebanon, but originated from the Islamic republic. Even though the Israelis have expressed that they will not intervene in this war, it does not keep Israel from giving Ukraine practical, useful intelligence that can help them with countermeasures for these drones.
The convergence of Iranian and Russian interests has constituted a long-lasting partnership characterized by anti-Western sentiments focusing on limiting NATO expansion, protecting and affirming the countries’ respective sovereignty, and enhancing military and technological capabilities. This partnership has materialized, across the years, through a constellation of hard and soft power measures, spacing from exchanges of weapons and military know-how on one hand to the common ideologically-based spread of disinformation and counter-narratives against common enemies on the other. As for now, the war in Ukraine provides new momentum to this allyship as the conflicts continue to evolve.
Whether the international community is effective vis-à-vis Iran and Russia also depends on the cohesiveness of their collective action. We have already witnessed a round of sanctions from the EU and the UK on Iranian drones in October 2022, precisely in response to their use on the Ukrainian conflict. As for the US, punitive measures targeting drones’ producers for Teheran have been issued as of three days ago. While Western power keeps a strict opposing stand against the Iranian-Russian allyship, China may emerge from this as a new mediating power between the two parts. The latter has already facilitated the recent agreement between Iran and Saudi Arabia to restore their diplomatic relations. It will discuss a possible resolution of the war in Ukraine with Spanish PM Sanchez in a soon-to-come meeting.
In the meantime, Iran’s supreme leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei continues to deny the Islamic Republic’s involvement in Ukraine. Accordingly, and in line with the anti-Western rhetoric previously mentioned, the official position reiterated by the Ayatollah is that the conflict in general was devised as a US-based diversion to justify NATO’s enlargements. As the UK gets ready to send armour-piercing rounds containing depleted uranium to Ukrainian forces, between the Kremlin, already protesting for the use of “nuclear weapons”, and the care recommendations of the UN on radioactive exposure, the conflict confirms to be yet another chessboard where the international power games unfold, with Iran and Russia playing on the same side.