Authors: Eline Stensen Gulliksen & Leif Niendorf - UK & European Affairs Team
Security in the Arctic
In recent years, the topic of Arctic security has gained significant attention in both scholarly and empirical circles. The Arctic's strategic value is derived from its geography, natural resources, shipping lanes, scientific research potential, and geopolitical influence. However, managing the Arctic is a complex task, as illustrated by conflicting territorial claims made by several countries. As a result, cooperation between multiple states is essential to safeguard and develop the region. The Arctic Council, composed of eight sovereign nations – Norway, Sweden, Finland, Iceland, Denmark, Russia, the USA, and Canada – has been established to promote such collaboration. A shift has been seen in how Arctic security is perceived, as it has putatively moved from Arctic Exceptionalism to a more geopolitically induced fragile situation. The full-scale invasion of Ukraine by Russia influenced this shift, pushing Sweden and Finish into NATO membership due to increased security concerns. This could potentially strengthen the alliance’s presence in the High North and alter the power balance in the Arctic creating increasing tension in the Arctic Council and beyond.
The notion of "Arctic exceptionalism" delineates the distinct characteristics of politics in the Arctic Council and, more broadly, in the region. This concept aligns with the constructivist approach to international relations, which prioritizes mutual ideas, customs, and values. Essentially, the notion maintains that cooperation trumps competition in the Arctic, where a zero-sum game prevails. Nevertheless, the idea of Arctic exceptionalism has elicited scepticism among scholars who believe it isolates the Arctic from global security discussions.
The Arctic Council experienced a notable shift in dynamics in 2014 when Russia annexed Crimea, marking a significant departure from the formerly shared ideals, standards, and identities towards a more practical and geopolitical perspective on global affairs. This shift underscores how the Arctic, once viewed as a unique region, is now impacted by contemporary international security issues and how any disputes beyond the area could affect collaboration within it. Hence, the applicability of the notion of Arctic exceptionalism can be increasingly questioned.
Recent developments in the European High North
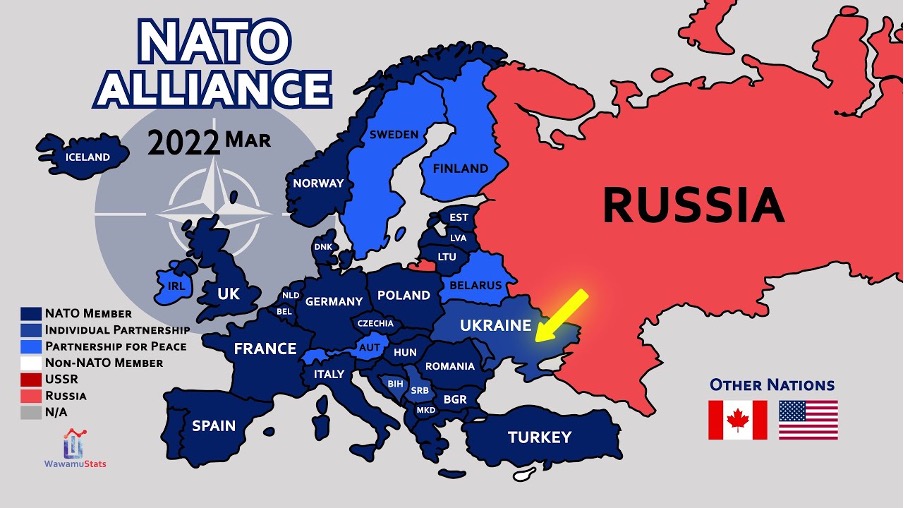
In March 2024 and April 2023 respectively, Finland and Sweden as two Arctic states joined NATO in direct response to Russia’s unprovoked full-scale war in Ukraine. It lucidly displays the interconnectedness of regional and global security dynamics, since the abatement of Arctic exceptionalism can be analyzed holistically, but also twofold, namely in terms of inherently regional security challenges and in the shadows of overall geopolitical competition in which China too, amid a race for raw materials, plays a role.
However, in the Northern European and Arctic regions themselves their accession might considerably change security dynamics and strategic proportions since not only the Baltic Sea is now a “NATO inlet“, but also out of the eight Arctic riparian states seven — all except Russia — are now NATO members, rendering Arctic security on this analytical level increasingly bipolar. This is all the more true for the continental European subsection of the Arctic.
The Arctic Council, interpretable as an institutionalised vehicle to uphold Arctic exceptionalism, is “absolutely not operating as normal“. After an initial full halt of cooperation, the seven resumed in the meanwhile to some cooperation without Russia. It can be conjectured that Finland’s and Sweden’s NATO membership further lowers the likelihood that it can return to its once-destined functionality (despite its disallowance to deal with military security). For scenario planners, even complete dissolution is on the table.
Beyond that, Sweden and Finland discontinue being buffer states between Russia and NATO for the largest part in the European High North whilst their strategic value is not to be underestimated. Although they don’t border the Arctic Ocean, there is now a broad and direct linkage between it and the Baltic Sea. Possibilities of regional reinforcements and deterrence are strengthened hereby. It is not to forget that the Kola Peninsula a key location of Russian strategic assets borders the North-Eastern corner of Europe. As there is talk about a “Militarisation of Russian Polar Politics“, Finland and Sweden could prove immensely helpful for NATO to counter such developments and A2/AD (anti-access/area denial) abilities of Russia in the region through own deterrence by denial.

Both countries bring remarkable capabilities with them into the alliance — Finland primarily on land and Sweden in the air — enhancing NATO’s capabilities to operate in the High North. Since, for the first time in history, all Nordic countries are now formally gathered under one collective defence structure, these can now also be further increased with a lower threshold in compound with their neighbours and long-standing NATO members Denmark and Norway. Already existing cooperation, for example within NORDEFCO, could now be substantially extended with positive effects on NATO’s posture in the High North.
The Swedish supreme commander moreover called for the establishment of a permanent military presence in the Arctic by his country. In the same vein, NATO Secretary General Jens Stoltenberg demanded to boost the alliance’s presence in the Arctic. With Sweden and Finland in, this experiences facilitation, also concerning exercises in hostile and cold environments. Russia’s confrontational behaviour in the meanwhile doesn’t suggest that it will simply swallow intensified NATO activity in the North European Arctic.
All this is overtly not too compatible with the informal agreement about Arctic exceptionalism that this pristine region shall exclusively be used for unwarlike purposes. This is not to say that Sweden’s and Finland’s accession to NATO solely and already had been the death blow to it, but new layers of security have been added that in tendency complicate the preservation of Arctic exceptionalism.
Conclusion
To summarize, Arctic exceptionalism is under threat. Both geopolitical and regional security dynamics could prove as challenging the notion of it. Sweden’s and Finland’s accession to NATO realistically impact the latter, especially in the European Arctic where NATO and Russia as adversaries are now drawn significantly closer to one another. The years we are in are possibly decisive for its endurance, which will be largely dependent on how NATO and Russia mutually evaluate their actions and their willingness to not sacrifice this unique part of the world to power games.
Nevertheless, to separate the European High North and wider Arctic and geopolitical discourses runs the risk of drawing an incomplete picture. Although regional analysis can be meaningfully carried out, it shall never be forgotten that it is an excerpt of broader security dynamics. The Arctic is nothing different in that, posing thus also a conceptual challenge to the idea of Arctic exceptionalism.