Author: Sarah Toubman
In the past few years, the Italian government has rapidly increased both the pace and number of steps taken to protect its national cybersecurity interests. Italy began creating legislation and organizations for the defense of its cybersecurity infrastructure in 1993, but many observers have criticized developments in Italian cybersecurity as inadequate and slow-moving compared to its peers in Europe and beyond. However, in June 2021, the Italian government declared its intention to create a new national agency for cybersecurity, and just weeks ago, released a national cybersecurity policy for 2022-2026.
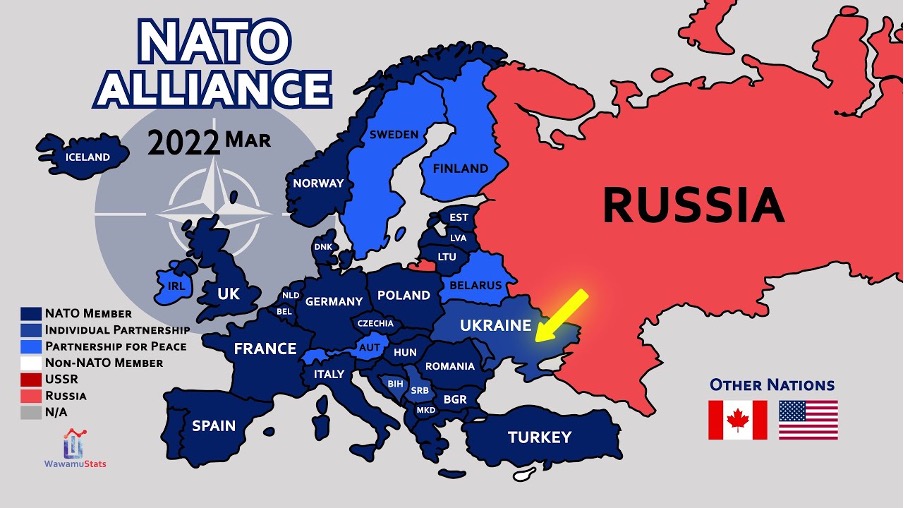
The Italian government’s increased attention to cybersecurity has come just in time, as several prominent cyberattacks against Italy by Russian hackers occurred this May. Considering Italy and the European Union’s support for Ukraine in its war against Russia, it is not surprising that Russian-backed agents have unleashed attacks on Italy in the cybersphere, a space the Kremlin has long operated in. For example, during the 2008 Ruso-Georgian war, Russian-backed hackers reportedly carried out cyberattacks against Georgian internet infrastructure.
More recently, this cyber aggression has been turned towards both state and private cyberinfrastructure in Italy. On May 10th, Russian hacker groups “Killnet” and “Legion” attempted to break into and modify the voting results for the Eurovision Song Contest, which Italy hosted and Ukraine ultimately won. However, thanks to the Italian Computer Security Incident Response Team, which was created in 2018, the attempt was foiled.
Similarly, just one day later on May 11th, “‘Killnet’ claimed an attack on the websites of several Italian institutions, including the Senate, Italy's upper house of parliament, and the National Health Institute.” On May 19th, the Russian hacking organization launched additional cyberattacks on Italian institutions, including the High Council of the Judiciary, and the Ministries of Foreign Affairs, Public Education, and Culture.
While Russian-backed cyber organizations are clearly enthusiastically targeting Italy, the robust responses of Italian cyber-defense organizations are now successful on a level which would have been unlikely prior to the development of its new cybersecurity agency and the rollout of its 2022-2026 cybersecurity policy. Although historically Italy has often been behind the curve in its cybersecurity policies, Mario Draghi’s push to launch the National Cybersecurity Agency was in fact extremely forward-looking and timely. Furthermore, since the agency’s announcement, Italian cybersecurity forces have developed the skills required to successfully counter Russian-backed agents, proving its creation was not merely a publicity-boosting measure for the Draghi government.
One recent headline has declared that “Italy [is] embroiled in cyber war with pro-Russian hackers.” Definitions of what constitutes cyberwarfare still vary, and the Russian government formally denies involvement with the groups of hackers conducting these attacks. However, such a headline again serves to remind those concerned with international security that Russia has historically and continues to use the cyber sphere to wage war, and therefore a robust international security policy necessarily includes cyber-defense. Therefore, in the context of the Russian invasion of Ukraine--the largest war seen in Europe since 1945--defensive cybersecurity capabilities are evermore important for Italy and any nation openly opposing Russian actions.
Italy’s 2013 National Strategic Framework for Cyberspace Security and 2017 Cybersecurity Action Plan had both highlighted the need for improved public-private cooperation to ensure national cybersecurity moving forward. In fact, the 2017 plan had urged that “private entities operating in strategic sectors must be considered as key assets and included into a holistic approach to national cybersecurity that provides for the implementation of minimum security requirements for country-critical systems.” Again, such a point was forward-looking, highlighting the fact that in May 2022, Russian-backed agents did not only launch cyberattacks on Italian government organizations, but also the Eurovision Song Contest, a multinational initiative being operated out of Italy.
Notably, under the country’s new cybersecurity policy, the Italian Computer Security Incident Response Team was successfully able to both prevent an attack against Eurovision and resolve cyber incidents related to government websites. However, moving forwards, this area merits even further attention. The Italian state could be severely impacted by cyberattacks against a whole range of websites, companies, and infrastructure, including public, private, and multinational organizations. Therefore, ensuring Italian cybersecurity going forward would require not just improved public-private cooperation, but also coordination between Italy and all interconnected sectors of the EU.
Italian translation
Negli ultimi anni, il governo italiano ha accelerato rapidamente il passo e ha compiuto progressi nella protezione dei suoi interessi nazionali nell’ambito della sicurezza cibernetica. L’Italia iniziò a legiferare e fondare organizzazioni per la difesa delle infrastrutture legate alla sicurezza cibernetica nel 1993. Da allora, molti osservatori hanno criticato gli sviluppi, ritenendoli inadeguati e lenti rispetto agli altri paesi in Europa e nel mondo. Giugno 2021 segna una tappa importante per il governo italiano, che dichiara di voler creare una nuova agenzia nazionale per la sicurezza cibernetica, e poche settimane fa, è stata pubblicata la policy per la sicurezza cibernetica nazionale 2022-2026.
L’aumento di attenzione per questo campo arriva perfettamente in tempo, quasi in concomitanza con diversi attacchi cibernetici compiuti da hacker russi contro l’Italia lo scorso Maggio. Tenendo presente il supporto dichiarato da Italia e Unione Europea per la guerra portata avanti dall’Ucraina contro la Russia, non è una sorpresa che agenti sostenuti dalla Russia stessa abbiano effettuato attacchi contro l’Italia nella sfera cyber, uno spazio in cui il Cremlino opera da tempo. Per esempio, durante la guerra tra Russia e Georgia nel 2008, la Russia ha dato supporto ad hacker per colpire le infrastrutture internet dell’avversario.
Più di recente, le aggressioni cyber sono state indirizzate contro la sfera cyber pubblica e privata dell’Italia. Il 10 Maggio, il gruppo hacker russo “Killnet” e “Legion” ha cercato di entrare e modificare i risultati dei voti dell’Eurovision Song Contest,tenutosi in Italia e vinto dall’Ucraina. Nonostante ciò, grazie al Computer Security Incident Response Team dell’Agenzia per la Cybersicurezza Nazionale, creato nel 2018, il tentativo è stato sventato.
Allo stesso modo, ad un solo giorno di distanza, “Killnet” ha rivendicato un attacco a diversi siti istituzionali italiani, incluso quello del Senato e dell’Istituto di Salute Nazionale. Il 19 Maggio, l’organizzazione russa ha lanciato ulteriori attacchi ad istituzioni italiane, inclusi il Consiglio Superiore della Magistratura, i Ministeri degli Affari Esteri, della Pubblica Istruzione e della Cultura.
Mentre le cyber organizzazioni russe sono chiaramente entusiaste di avere l’Italia come bersaglio, le risposte robuste date dalle organizzazioni di cyber-difesa italiane hanno avuto un successo che non sarebbe stato possibile raggiungere precedentemente allo sviluppo della nuova Agenzia per la Cybersicurezza Nazionale e alla nuova policy 2022-2026. Sebbene storicamente l’Italia si è sempre trovata in ritardo rispetto ai progressi e alle policy promosse dagli altri paesi, il Presidente Mario Draghi ha insistito per fondare l’Agenzia per la Cybersicurezza Nazionale e questo ha permesso di essere estremamente lungimiranti nel garantire una risposta agli attacchi. Inoltre, dalla creazione dell’Agenzia, l’Italia ha sviluppato delle abilità notevoli e necessarie nella lotta contro gli agenti russi.
Di recente, è stato dichiarato che “l’Italia è coinvolta in una cyber guerra con gli hacker russi.” Le definizioni di questa cyber-guerra sono ancora varie, e il governo russo ha formalmente negato il coinvolgimento dei gruppi hacker e gli attacchi condotti. Nonostante questo, la situazione al momento conferma che la sfera cyber è sempre utilizzata dalla Russia come arma contro i nemici di guerra, e perciò c’è bisogno di politiche per la sicurezza internazionale più robuste e che includano necessariamente la cyber difesa. Nella guerra tra Russia e Ucraina, la più grande guerra mai vista dopo il 1945, le capacità difensive nel campo della cybersicurezza sono ancora più significative per l’Italia e per qualunque altra nazione che voglia apertamente condannare le azioni Russe.
La National Strategic Framework for Cyberspace Security del 2013 e il Cybersecurity Action Plan del 2017 hanno entrambi sottolineato il bisogno di migliorare la cooperazione tra pubblico e privato per assicurare una rapida evoluzione nell’ambito della cyber sicurezza nazionale. Infatti, il piano del 2017 ha evidenziato che “le entità private che operano per la cyber sicurezza nazionale lavorano per l’implementazione dei minimi standard di sicurezza richiesti per le infrastrutture critiche del paese.” Ancora una volta, questo punto di vista è lungimirante e sottolinea il fatto che a Maggio 2022, gli agenti russi non hanno solo colpito il governo italiano ma anche l’Eurovision Song Contest, un’iniziativa multinazionale che era organizzata dall’Italia.
Il Computer Security Incident Response Team dell’Italia ha avuto successo nel prevenire l’attacco contro l’Eurovision e nel risolvere incidenti legati a siti internet del governo.
Infine, questo argomento meriterebbe ancora più attenzione. Lo stato italiano potrebbe essere severamente colpito da cyber attacchi contro siti internet, compagnie e infrastrutture, includendo il settore pubblico, privato e organizzazioni multinazionali. Per questo, garantire la cyber sicurezza del paese e svilupparla ulteriormente richiederebbe non solo un miglioramento della cooperazione tra pubblico e privato, ma anche la coordinazione tra Italia e tutti i settori interconnessi dell’Unione Europea.